Category: Alternative Investment Strategy
Trend-following is not the same as following the herd of opinions
Investors may be viewed as trend-follower because they chase performance, only picks recent winners, and sort on performance. However, trend-following professionals often exploit this undisciplined, casual, and unsystematic approach to trends through the investment scaling of chasers. Investor behavior driven by tracking the opinion of peers is a form of trend following and may create price trends; however, it is not the same as a disciplined approach to finding trade opportunities through rules-based behavior.
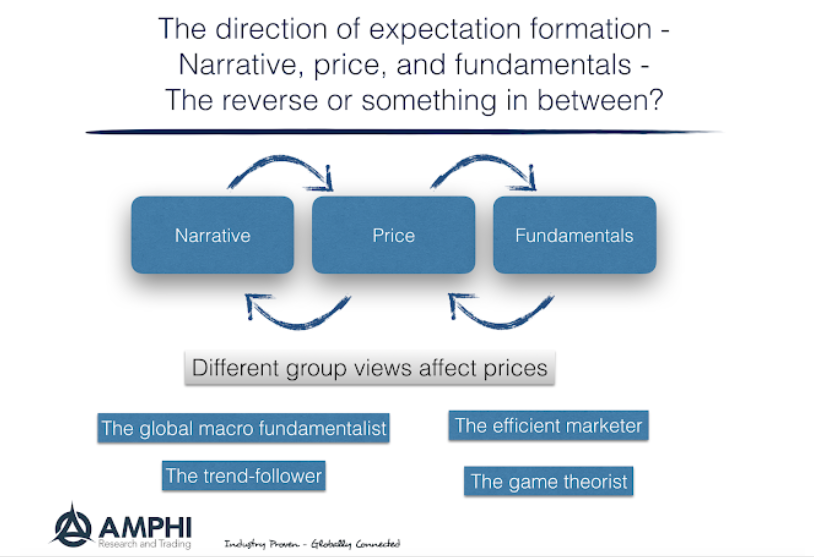
Mastering Market Philosophy: How Your Investment Strategy Shapes Your Profits
Any investor needs to know two things: what is the philosophy that drives his decisions; what is the philosophy that is driving the market as a whole. Are you price, fundamental, efficiency or narrative driven? Is the market currently price, fundamental, or narrative driven? Know your expectation mechanics.
That’s crisis not correction alpha, you fool! Trend-following value is in simplicity
I discovered from reading an informative piece on managed futures and CTA’s from HedgeNordic magazine that trend-followers will produce “crisis alpha” but not “correction alpha”. A crisis is defined as a significant and extended downturn while a correction is short-term drawdown. Unfortunately, one man’s correction is another man’s crisis. All crises start and end as corrections.
FX intervention – Analysis says central bank activity works
Many have held the view that central bank FX intervention is ineffective. It can be disruptive and have some temporary impact, but central banks cannot make currency markets do what they don’t want to do. Research using public data, a limited sample and mainly focused on floating exchange rate regimes, shows, at best, mixed value […]
Alternative risk premia overreaction in 2018 – Don’t fall for recency bias
What happened to alternative risk premia returns in 2018? This was a major discussion topic at a UBS risk premia conference last week. It was a difficult year. In fact, it was the worst performance year since 2008, and the decline for many strategies was a multiple standard deviation event. Yet, there is a good opportunity for investors who focus on the longer-run. Since the performance for many risk premia seemed unrelated to macro factors, there is strong potential for mean reversion to longer-term strong positive performance. To extrapolate recent performance as representative of history would be to fall into a recency bias.
Risk premia performance generally positive for January
It is a new year and the underperformance of many alternative risk premia strategies in 2018 is now an old memory. Good performance heals past return wounds. While well-constructed alternative risk premia should not be highly correlated to market beta, they will be related to the investment regime. Risk premia are time varying.
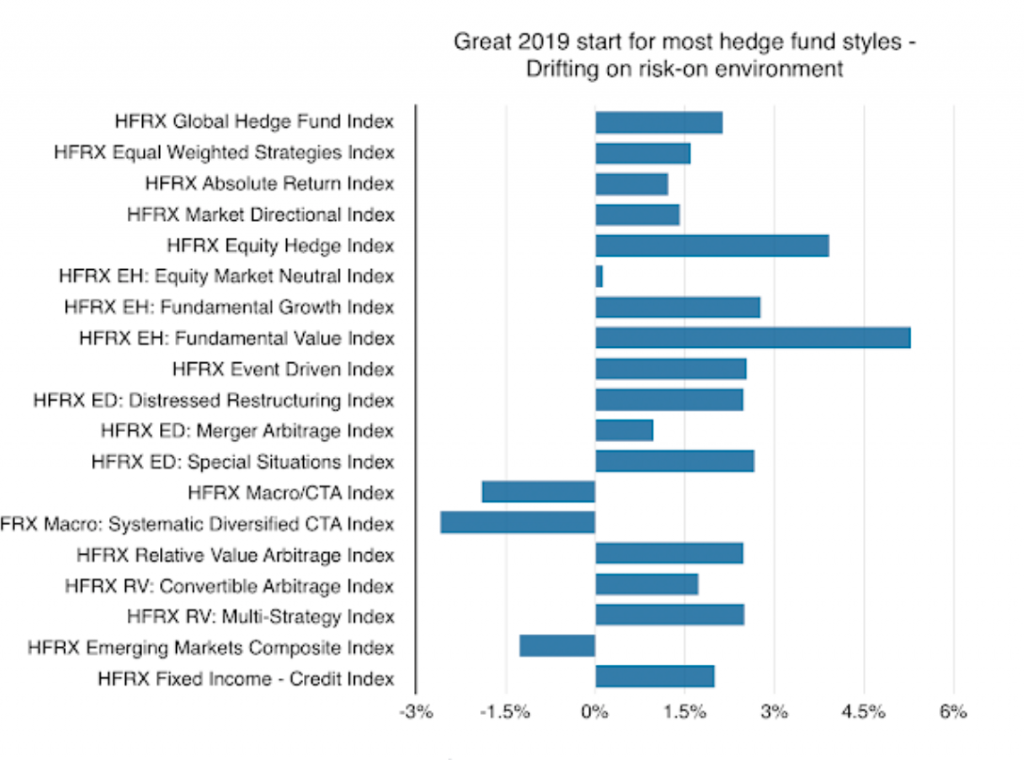
A risk-on environment and the hedge fund world is good
Hedge fund styles as measured by the HFR indices showed strong positive January performance in tandem with the gains in the stock market. When in a risk-on environment many hedge fund styles are winners.
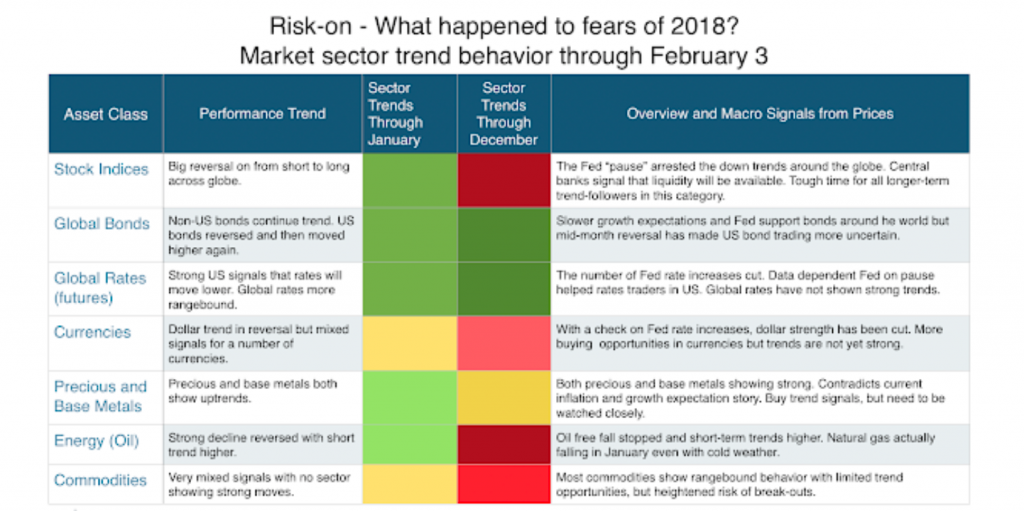
Risk-on- What happened to fears of 2018?
The equity reversal was tough on many trend-followers. This reversal spilled-over to US bonds during the month. Good buy trend signals now in both equities and bonds. Dollar strength reversed on Fed pause remarks. Metals and energy both moved higher during the month even with global growth threats. Commodities asset class is not a trend rich environment at this time.
Global stocks – All about avoiding global slowdowns and recessions
Is it that simple? Global equity investing is all about missing the big macro risks – recessions. There are headline risks every year, but it is always about economic growth when you step-back and look at annual performance. If global growth appreciably slows, global stocks are hurt. A simple long-only asset allocation strategy is to stick with long-term trends with the ability to walk-away when a recession or slowdown occurs.
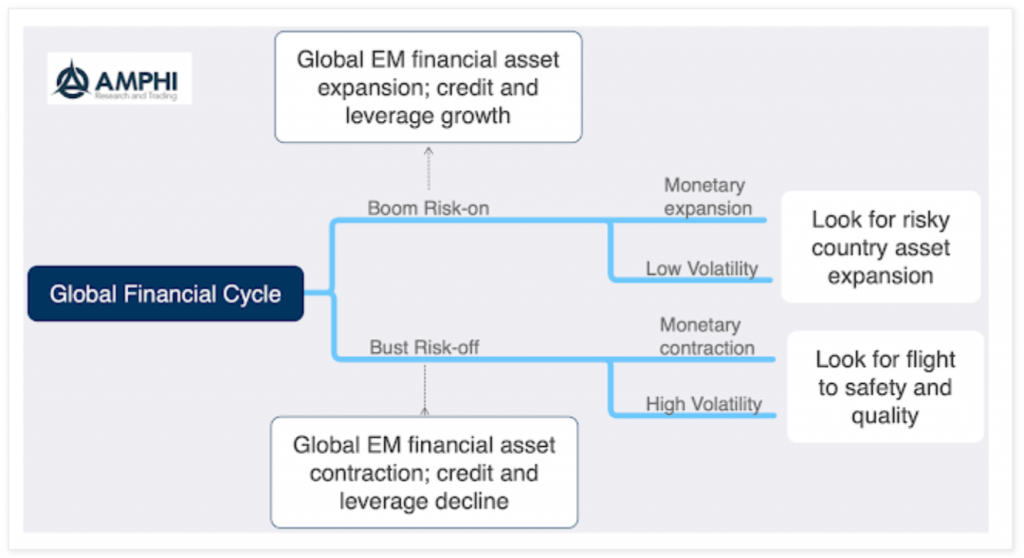
Global Financial Cycle – Look for the risk regimes
A recurring theme for our forecasting model is not predicting the future but just identifying the current regime. It is more important to first know where you are before you determine where you might be going. If you have ever been lost, the best solution is to first figure out your current location.
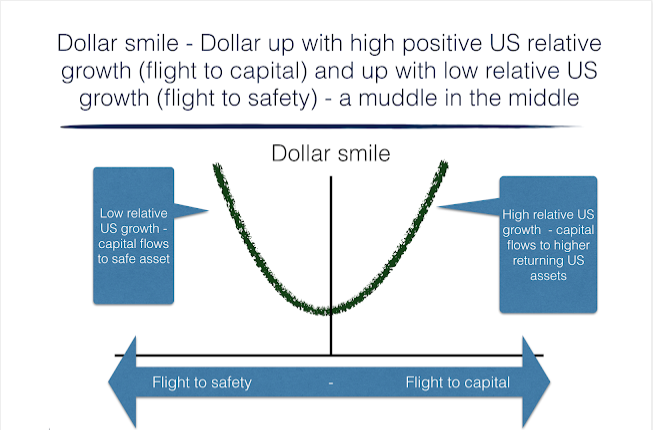
Dollar smile – We are moving to the smile bottom
A good simple approach for framing the longer-term movements in the dollar is through using the narrative of a dollar smile. We have written about this years ago, but think it is relevant today. The dollar smile, first popularized by Stephen Jen, says that currency behavior is driven by two competing regimes. Regime 1 is […]
Concentration, inequality and the status quo – Size matters but not always for the better
A capitalist system is not always competitive environment, but competitive environment is a capitalist system. One key macro issue that is not often discussed is the increasing concentration of businesses in the US and other capitalist countries. While not monopolies, an increasing amount of market share is in the hands of fewer companies and form oligopolies.
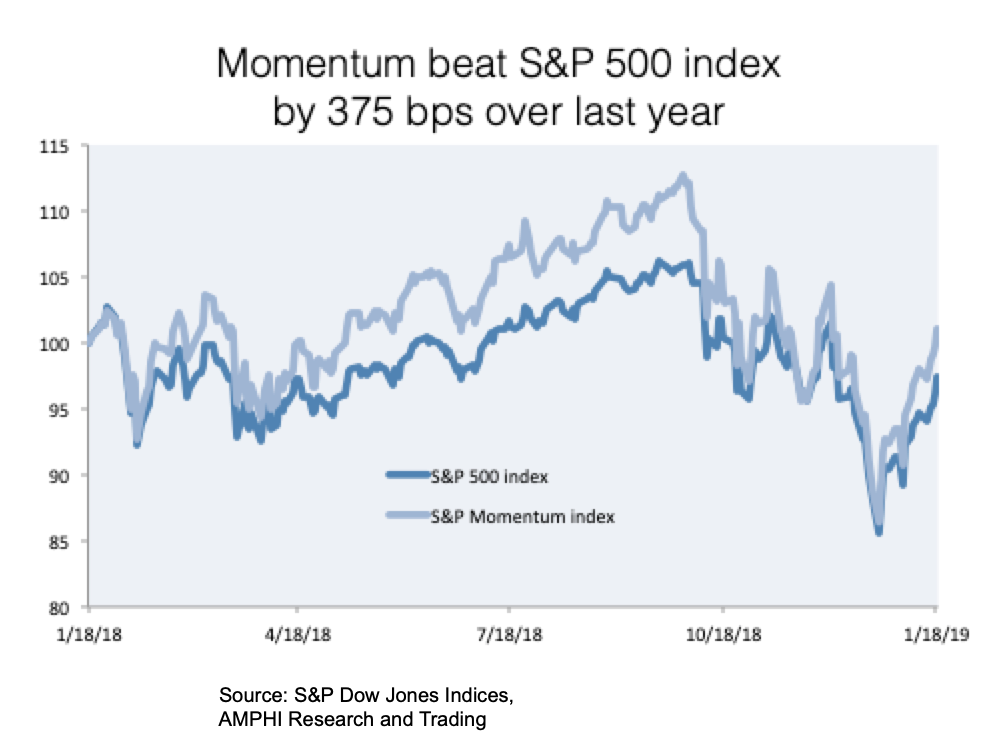
Momentum is still a viable strategy – Look at the numbers
There has been a lot of discussion on the lack of success with momentum and trend-following strategies. There is little doubt that there has been greater dispersion in returns across managers. There have been winners and losers with disappointment focused on some larger high profile firms.