Archives
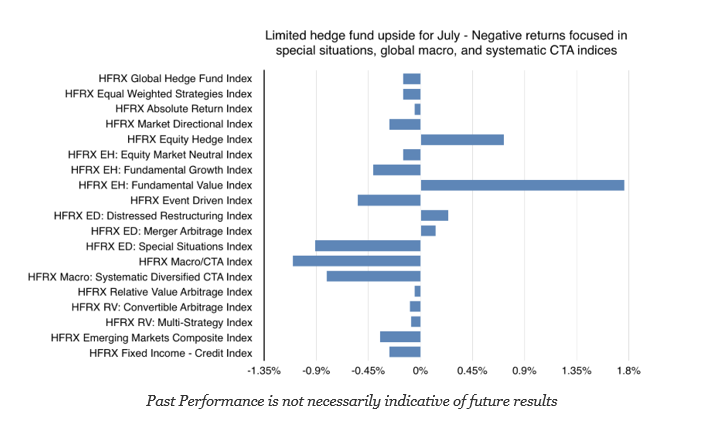
Hedge Fund Performance Mixed for July
Hedge fund returns for July were generally negative with the only exceptions being equity hedge and fundamental value strategy indices. The class of uncorrelated hedge funds styles, event driven and special situations, under performed. Defensive styles like systematic CTA and global macro also posted negative returns.
Switch To Risk-On But Dispersion In Return Shows Mixed Opportunities
All equity style sectors generated gains for July. The EM index ETF is the only major style down for the year. Global markets outperformed more localized US markets as measured by mid and small cap indices. Growth has been the best style index this year with returns exceeding 11 percent. While performing well this month, global equities have still lagged for the year based on growth and earnings differentials versus the US. Nevertheless, there are some concerns about short-term trends in smaller cap indices as well as growth and value indices.
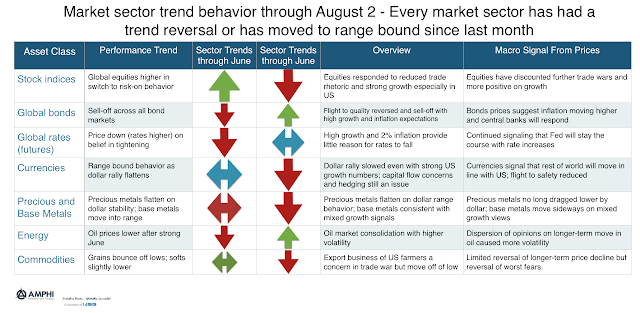
Sector Trends Show Significant Changes Over Last Month
Our tracking models for the end of July show that there have been changes in direction for all major sectors. This would usually suggest significant loses for trend managers but the relatively mild volatility and the slow reversals allowed for adjustment of signals to mitigate loses.
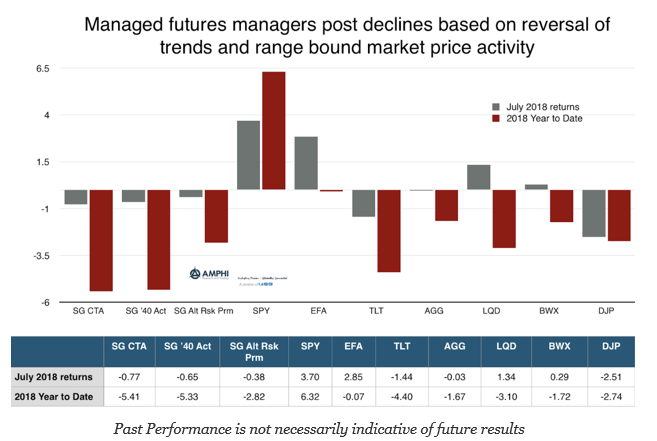
If There Are No Trends, There Will Be No Gains – Managed Futures Slightly Negative On Range Bound Market Behavior
July proved to be a classic reversal from less risk appetite to risk-on behavior. Global equities, which were weak in June, reversed on the expectations of stronger growth and earnings. This was bad news for trend-followers positioned for further market declines. The switch in risk appetite caused bonds to move lower. The strong growth, higher inflation, expected larger supplies, and expectations for continued Fed QT placed added pressure on Treasuries. Credit markets moved in-line with equities. The range bound currencies helped international assets but did not allow for trading gains. Commodities were mixed with energy prices moving lower and grains seeing some buying pressure after large declines last month. All of these reversals did not help intermediate trend traders.
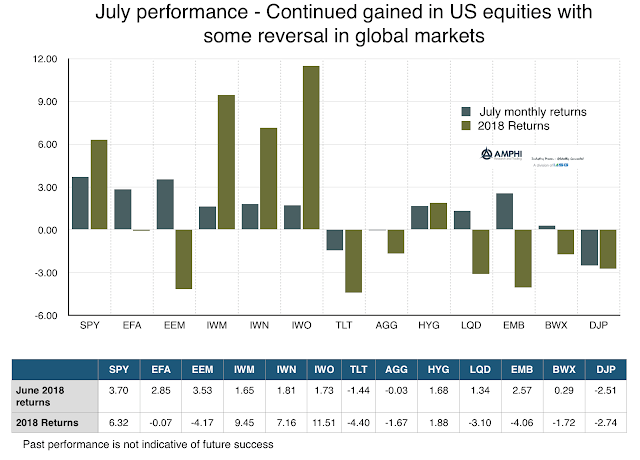
July Performance Shows Risk-On Appetite
First look at the data to see what weighted market opinion is telling us. July marks a reversal to more risk-on behavior with strong gains in large cap US stocks as well as international and emerging market equities. While small cap, growth, and value indices all did well, the broader international concerns affecting risk behavior have abated. This positive global view was also seen in the international bond markets. The dollar rise from a desire for safety was contained and more range bound. Along with international bonds, credit markets improved with tightening spreads. The only losers for the bond sector were long-duration Treasuries and commodities.
The Correlation within the Financial Cycle – Not Good for Those Looking for International Diversification
One of the core strategies for portfolio diversification is increasing exposure to international stocks and bonds. This risk reduction strategy is easy to achieve, yet the value of this asset class diversification has diminished over the last few years. The financial cycle has more commonality as measured through times series analysis, and it is harder […]
“Strong Opinions, Weakly Held” – Use it as a Guide to Help Make Better Decisions
Allow your intuition to guide you to a conclusion, no matter how imperfect — this is the “strong opinion” part. Then –and this is the “weakly held” part– prove yourself wrong. Engage in creative doubt. Look for information that doesn’t fit, or indicators that pointing in an entirely different direction. Eventually your intuition will kick in and a new hypothesis will emerge out of the rubble, ready to be ruthlessly torn apart once again. You will be surprised by how quickly the sequence of faulty forecasts will deliver you to a useful result. – Paul Saffo
The Overton Window and Finance – Thinking through the Process from Extreme Views to Acceptance
The Overton Window is called the window of discourse for any range of ideas. It has mostly been used to describe differences in political discussions. Extreme views will be unacceptable, but as they are either adjusted or gain traction, there is a window of acceptance or common ground between extremes. The viability of any idea is determined by whether it falls into the window between extremes. Any idea is constrained if it falls out side the window.
Mistakes Will Be Made – Just Don’t Make Any on Purpose
Mistakes were made. Mistakes will be made. Sorry, I made a mistake. Many think that an apology for mistakes is all forgiving. But the definition or type of mistake makes all the difference. Don’t make them on purpose.
Spend Your Time On “What Is”, Not “What If”
Spend your time on “what is”, not “what if”. I picked up the phrase from The 10 Pillars of Wealth by Alex Becker. It seems apt given many recent discussions on the global economic environment. I am a strong believer in scenario analysis and have talked about scenarios as good tools even for trend-followers to assess potential risks, yet there is a hidden or implicit assumption that is more important for any financial discussion – what is the current environment.
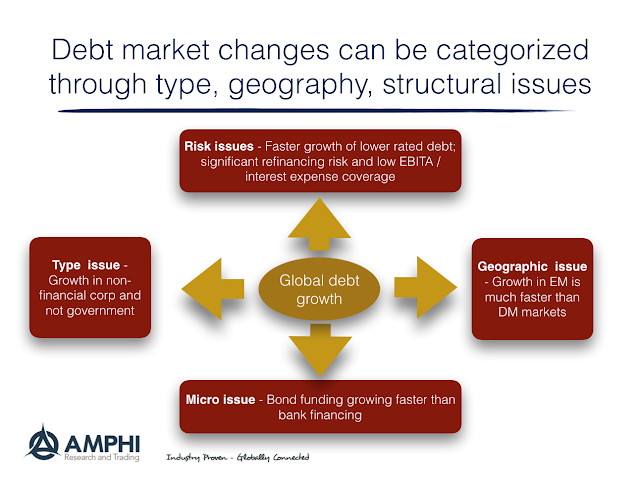
Debt – “If Something Cannot Go on Forever, It Will Stop” – The Problem Is Not If But, Figuring Out When
The McKinsey Global Institute published a new report, Rising Corporate Debt: Peril or Promise?, that is good reading for anyone focused on global debt issues. The charts and tables provide a wealth of data.
Keynes on Money – Do Not Hold Any as a Store of Value
“…for it is a recognized characteristics of money as a store of wealth that it is barren; whereas practically every other form of storing wealth yields some interest or profit. Why should anyone outside a lunatic asylum wish to use money as a store of wealth.
Because, partly on reasonable and partly on instinctive grounds, our desire to hold money as a store of wealth is a barometer of the degree of our distrust of our own calculation and conventions concerning the future.”
-Keynes
Focus on the Dislocations – These are the Places of Market Opportunity this Week
There are some recurring themes this week in our highlighted charts, debt and leverage will overhang any global economic discussion; however, we see some interesting dislocations that can offer global macro opportunities: